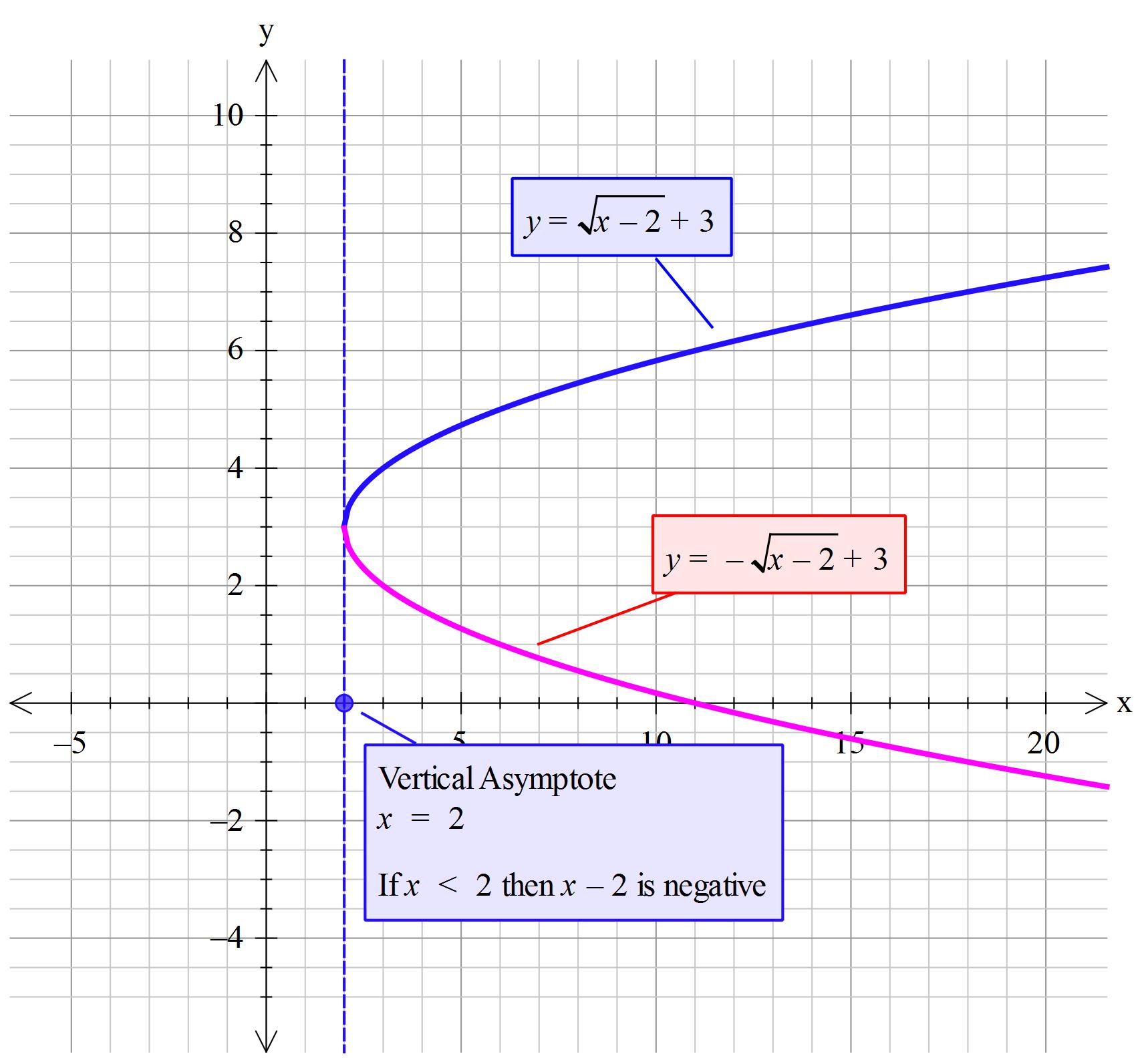
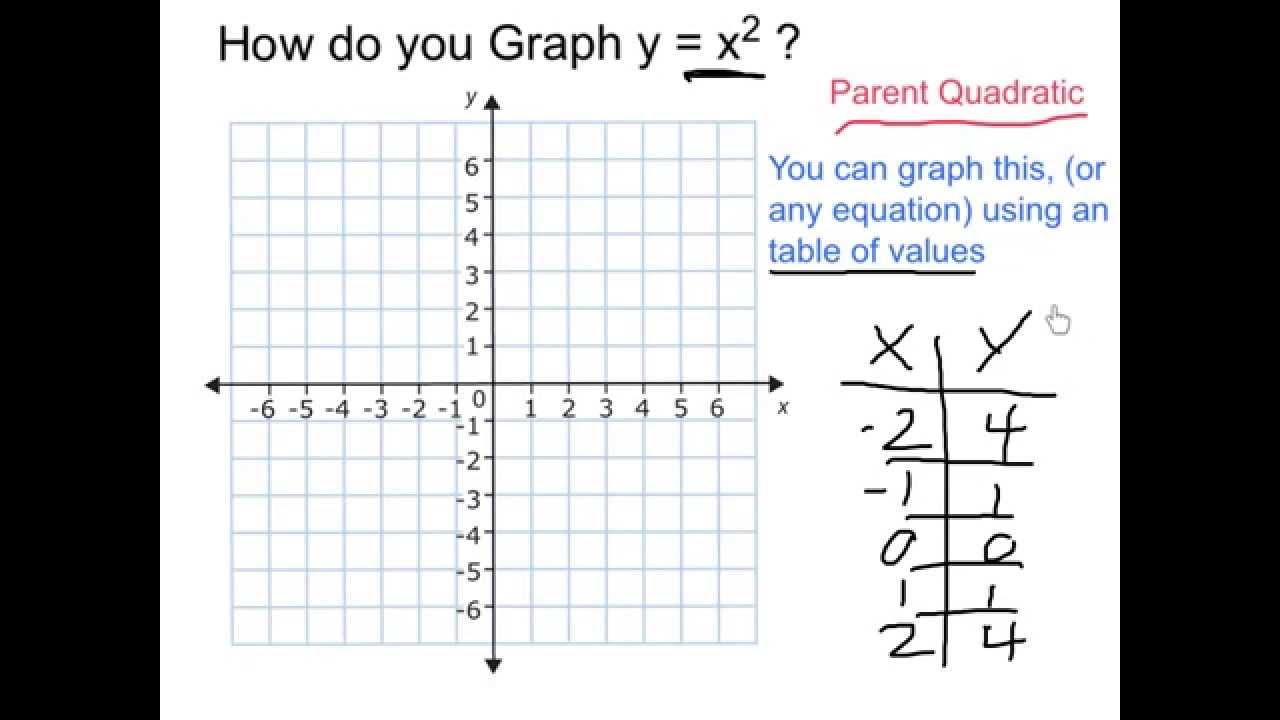
How Do You Graph Y Sqrt X 2 3 Socratic
#at least simply put Don't up resolutionIt will plot functions given in the form y = f(x), such as y = x 2 or y = 3x 1, as well as relations of the form f(x,y) = g(x,y), such as x 2 y 2 = 4 To use the plot command, simply go to the basic plot page , type in your equation (in terms of x and y), enter the set of x and y values for which the plot should be made and hit the "Plot
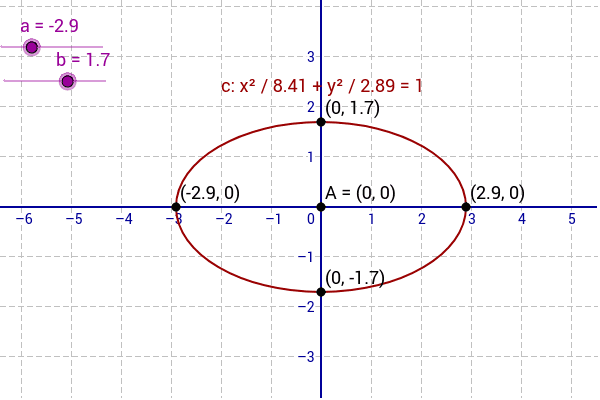
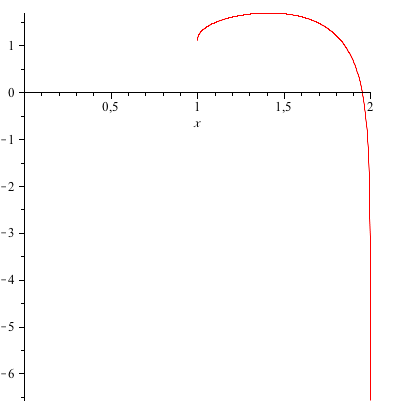
Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1
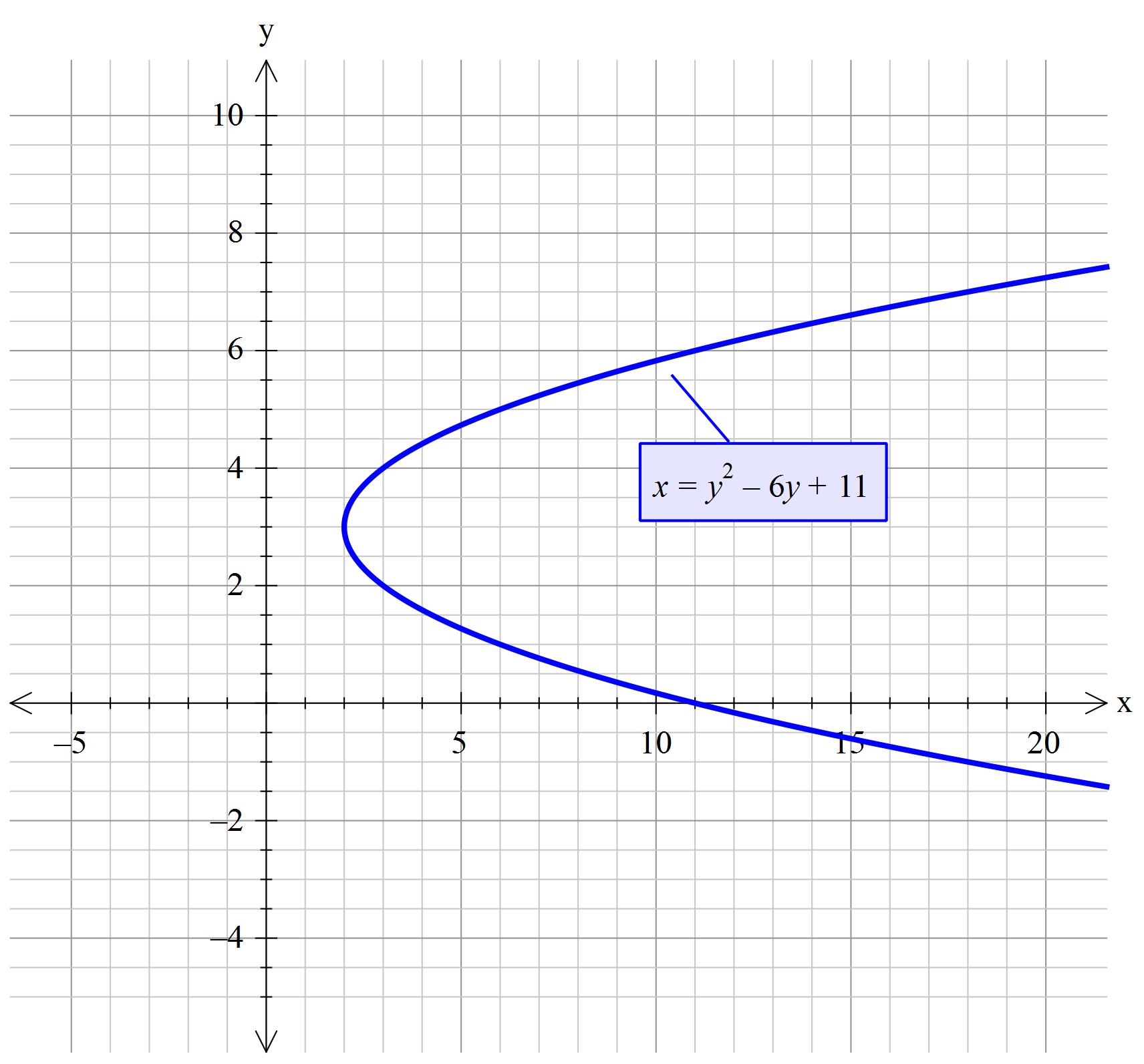
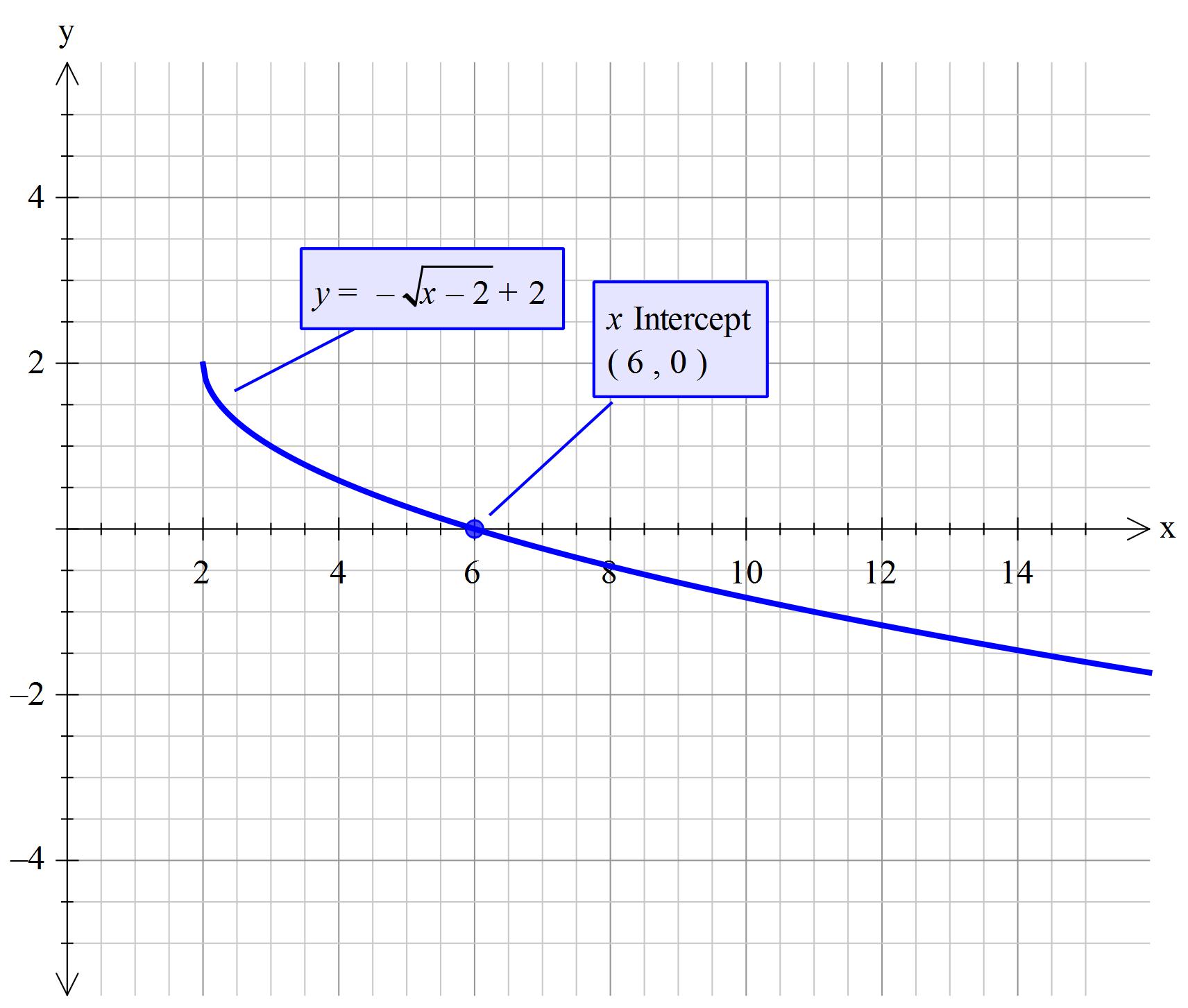
Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1-Graph the parabola, y =x^21 by finding the turning point and using a table to find values for x and y So the first one will be y 1 = √(x − 2) and the second one is y 2 = −√(x − 2) When you graph these on the same axis, it will give the required result nimitz says at 1142 am Comment permalink thanks i know it nandan says at 958 pm Comment permalink very good

Graphing Parabolas
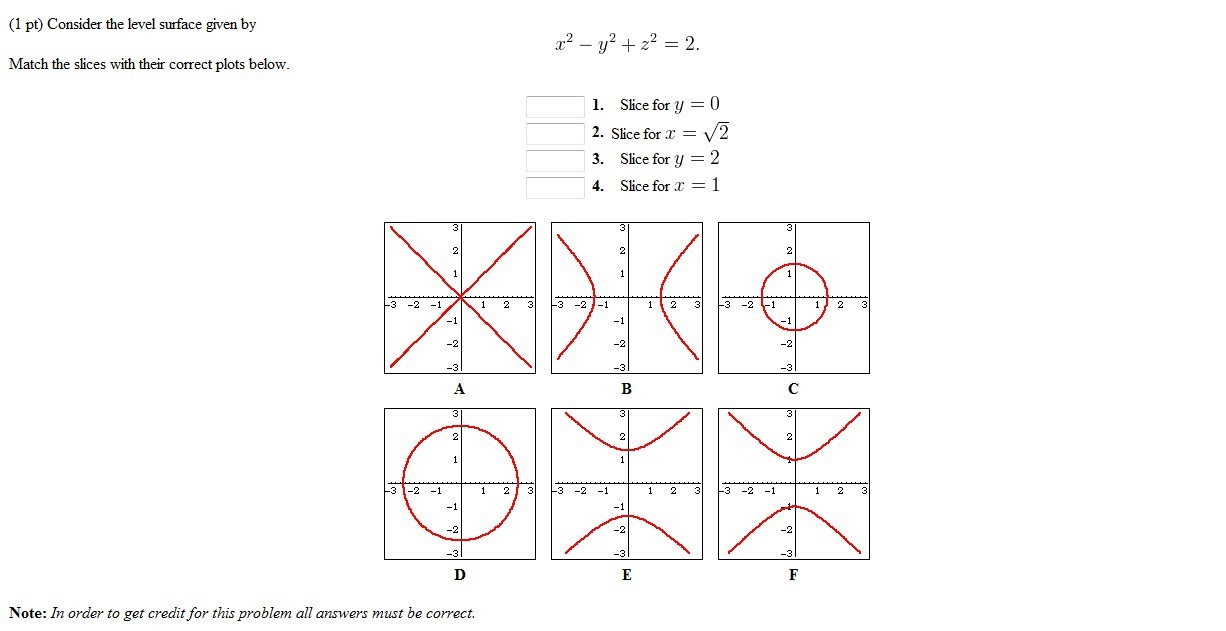
First, substitute r 2 = x 2 y 2 into the given equation r 2 z 2 = 9 in order to arrive to its rectangular form r 2 = x 2 y 2 r 2 z 2 = 9 x 2 y 2 z 2 = 9 The resulting equation is a sphere centered at the origin with radius 3 Answer Therefore, θ = π/2 is a halfplane and r If you subtract one side of the equation from the other, so the solutions are at 0, you can use outer to calculate a grid of z values, which contour can then plot x < seq (2, 2, by = 001) # high granularity for good resolution z < outer (x, x, FUN = function (x, y) x^2*y^3 (x^2y^21)^3) # specify level to limit contour lines printed contour (x, x, z, levels = 0)Sin (x)cos (y)=05 2x−3y=1 cos (x^2)=y (x−3) (x3)=y^2 y=x^2 If you don't include an equals sign, it will assume you mean " =0 " It has not been well tested, so have fun with it, but don't trust it If it gives you problems, let me know Note it may take a few seconds to finish, because it has to do lots of calculations
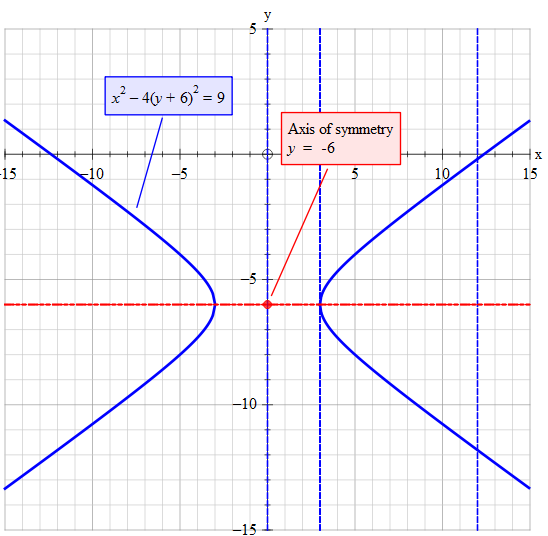
Exercise 2(a) y = √ 4x4 can be reexpressed as follows Subtract 4 from each side y −4 = √ 4x y −4 = 2 √ x y −4 = 2x12 Taking logarithms of each side yields log(y −4) = 1 2 log(x)log(2) Thus plotting log(y−4) against log(x) would give a straight line with slope 1 2 and intercept log(2) on the log(y −4) axis Click on theI Limits in y 0 6 y 6 √ 4 − x2, so the positive side of the disk x2 y2 6 4 I Limits in z 0 6 z 6 p 4 − x2 − y2, so a positive quarter of the ball x2 y2 z2 6 4 2 z x y 2 2 Triple integral in spherical coordinates Example Change to spherical coordinates and compute the integral I = Z 2 −2 Z √ 4−x2 0Cos(x^2) (x−3)(x3) Zooming and Recentering To zoom, use the zoom slider To the left zooms in, to the right zooms out When you let go of the slider it pltplot(x, y, linewidth=) Use the setter methods of a Line2D instance plot returns a list of Line2D objects;Precalculus Graph x^2 (y1)^2=1 x2 (y − 1)2 = 1 x 2 ( y 1) 2 = 1 This is the form of a circle Use this form to determine the center and
Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
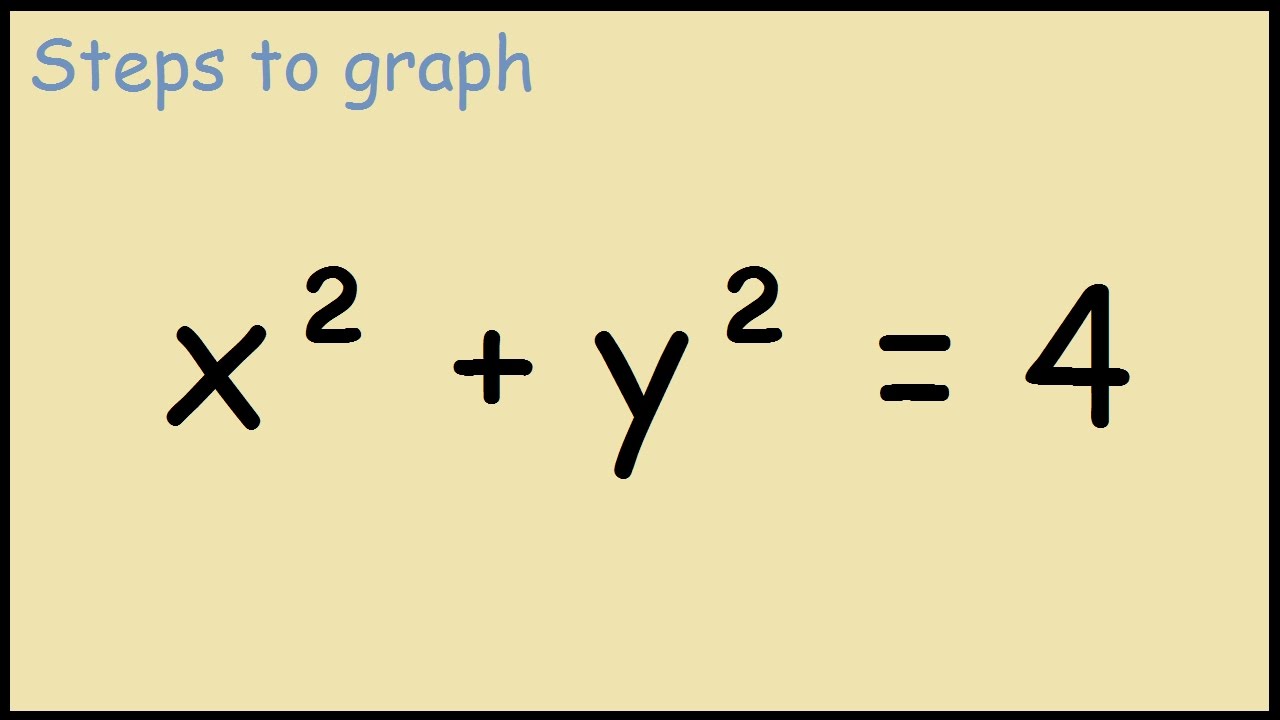 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Plot x2 (y-√ x )2=1」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
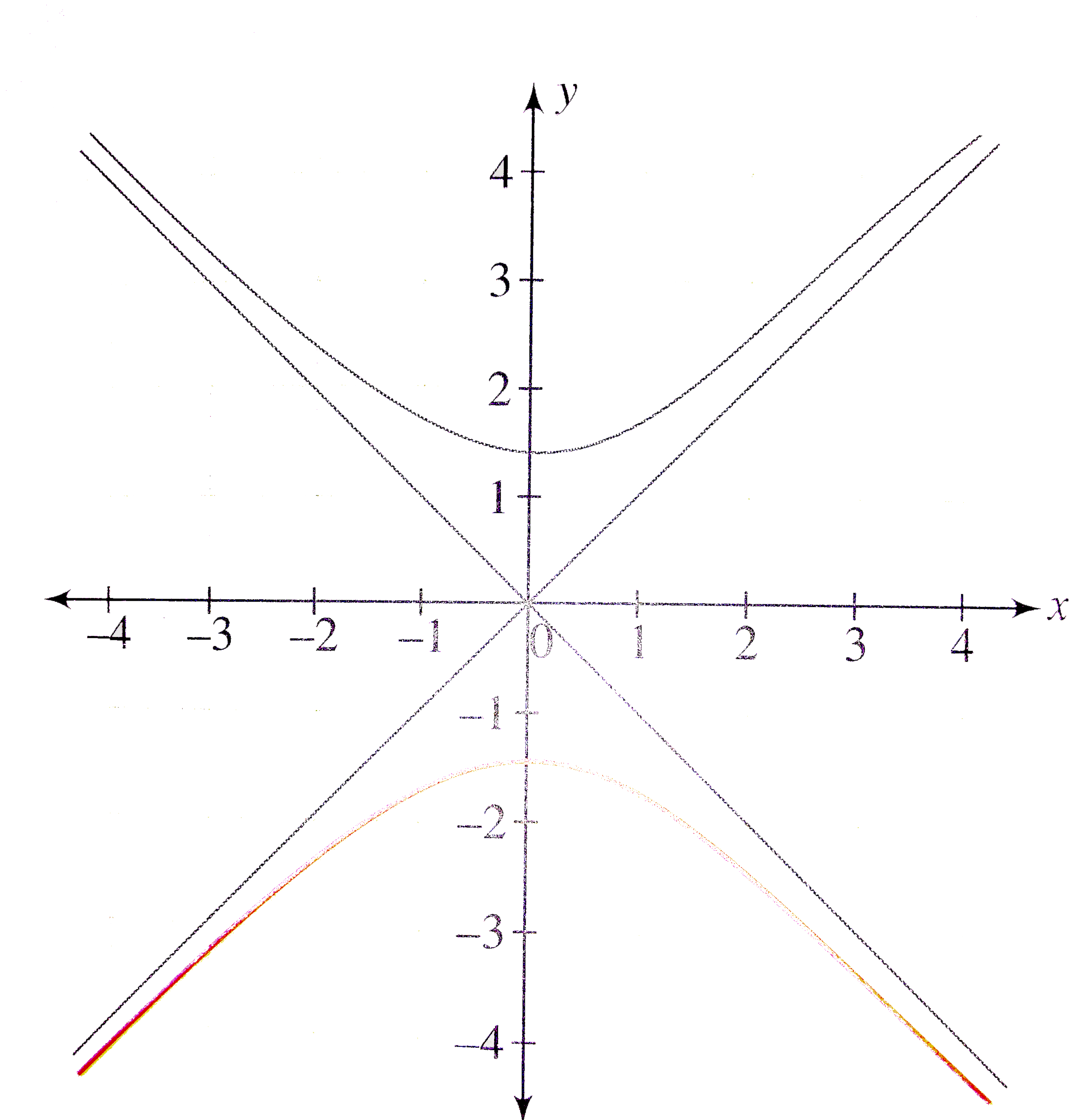
Cos(x^2) (x−3)(x3) Zooming and Recentering To zoom, use the zoom slider To the left zooms in, to the right zooms out When you let go of the slider it goes back to the middle so you can zoom more Sign (1 or −1) of aEnter {piecewisedefined {\left(\sqrt{x} 2\right) 1}{x}\right) = 0$$ Let's take the limit so, inclined coincides with the horizontal asymptote on the left Even and odd functions Let's check, whether the function even or odd by





0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿